By Emily Badger, Claire Cain Miller, Adam Pearce and Kevin Quealy, New York Times —
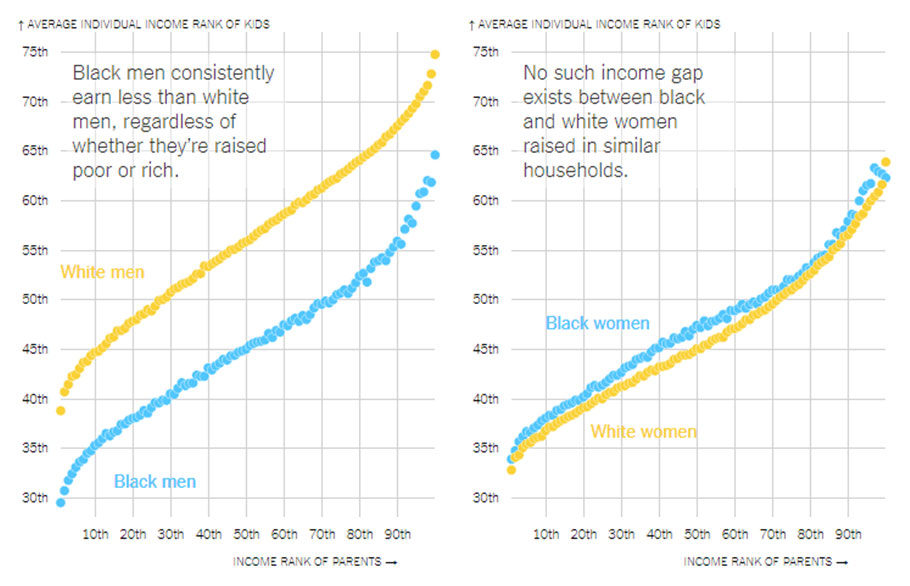
Black boys raised in America, even in the wealthiest families and living in some of the most well-to-do neighborhoods, still earn less in adulthood than white boys with similar backgrounds, according to a sweeping new study that traced the lives of millions of children.
White boys who grow up rich are likely to remain that way. Black boys raised at the top, however, are more likely to become poor than to stay wealthy in their own adult households.
 Even when children grow up next to each other with parents who earn similar incomes, black boys fare worse than white boys in 99 percent of America. And the gaps only worsen in the kind of neighborhoods that promise low poverty and good schools.
Even when children grow up next to each other with parents who earn similar incomes, black boys fare worse than white boys in 99 percent of America. And the gaps only worsen in the kind of neighborhoods that promise low poverty and good schools.
According to the study, led by researchers at Stanford, Harvard and the Census Bureau, income inequality between blacks and whites is driven entirely by what is happening among these boys and the men they become. Black and white girls from families with comparable earnings attain similar individual incomes as adults.
Large income gaps persist between men — but not women.
“You would have thought at some point you escape the poverty trap,” said Nathaniel Hendren, a Harvard economist and an author of the study.
Black boys — even rich black boys — can seemingly never assume that.
The study, based on anonymous earnings and demographic data for virtually all Americans now in their late 30s, debunks a number of other widely held hypotheses about income inequality. Gaps persisted even when black and white boys grew up in families with the same income, similar family structures, similar education levels and even similar levels of accumulated wealth.
The disparities that remain also can’t be explained by differences in cognitive ability, an argument made by people who cite racial gaps in test scores that appear for both black boys and girls. If such inherent differences existed by race, “you’ve got to explain to me why these putative ability differences aren’t handicapping women,” said David Grusky, a Stanford sociologist who has reviewed the research.
A more likely possibility, the authors suggest, is that test scores don’t accurately measure the abilities of black children in the first place.
If this inequality can’t be explained by individual or household traits, much of what matters probably lies outside the home — in surrounding neighborhoods, in the economy and in a society that views black boys differently from white boys, and even from black girls.
“One of the most popular liberal post-racial ideas is the idea that the fundamental problem is class and not race, and clearly this study explodes that idea,” said Ibram Kendi, a professor and director of the Antiracist Research and Policy Center at American University. “But for whatever reason, we’re unwilling to stare racism in the face.”
The authors, including the Stanford economist Raj Chetty and two census researchers, Maggie R. Jones and Sonya R. Porter, tried to identify neighborhoods where poor black boys do well, and as well as whites.
“The problem,” Mr. Chetty said, “is that there are essentially no such neighborhoods in America.”
The few neighborhoods that met this standard were in areas that showed less discrimination in surveys and tests of racial bias. They mostly had low poverty rates. And, intriguingly, these pockets — including parts of the Maryland suburbs of Washington, and corners of Queens and the Bronx — were the places where many lower-income black children had fathers at home. Poor black boys did well in such places, whether their own fathers were present or not.
Share of children living in low-poverty neighborhoods with many fathers present
 Share of children living in high-poverty neighborhoods with few fathers present
Share of children living in high-poverty neighborhoods with few fathers present
 “That is a pathbreaking finding,” said William Julius Wilson, a Harvard sociologist whose books have chronicled the economic struggles of black men. “They’re not talking about the direct effects of a boy’s own parents’ marital status. They’re talking about the presence of fathers in a given census tract.”
“That is a pathbreaking finding,” said William Julius Wilson, a Harvard sociologist whose books have chronicled the economic struggles of black men. “They’re not talking about the direct effects of a boy’s own parents’ marital status. They’re talking about the presence of fathers in a given census tract.”
Other fathers in the community can provide boys with role models and mentors, researchers say, and their presence may indicate other neighborhood factors that benefit families, like lower incarceration rates and better job opportunities.
The research makes clear that there is something unique about the obstacles black males face. The gap between Hispanics and whites is narrower, and their incomes will converge within a couple of generations if mobility stays the same. Asian-Americans earn more than whites raised at the same income level, or about the same when first-generation immigrants are excluded. Only Native Americans have an income gap comparable to African-Americans. But the disparities are widest for black boys.
 “This crystallizes and puts data behind this thing that we always knew was there because we either felt it ourselves or we’ve seen it over time,” said Will Jawando, 35, who worked in the Obama White House on My Brother’s Keeper, a mentoring initiative for black boys. Even without this data, the people who worked on that project, he said, believed that individual and structural racism targeted black men in ways that required policies devised specifically for them.
“This crystallizes and puts data behind this thing that we always knew was there because we either felt it ourselves or we’ve seen it over time,” said Will Jawando, 35, who worked in the Obama White House on My Brother’s Keeper, a mentoring initiative for black boys. Even without this data, the people who worked on that project, he said, believed that individual and structural racism targeted black men in ways that required policies devised specifically for them.
Mr. Jawando, the son of a Nigerian father and a white mother, grew up poor in Silver Spring, Md. The Washington suburb contains some of the rare neighborhoods where black and white boys appear to do equally well. Mr. Jawando, who identifies as black, is now a married lawyer with three daughters. He is among the black boys who climbed from the bottom to the top.
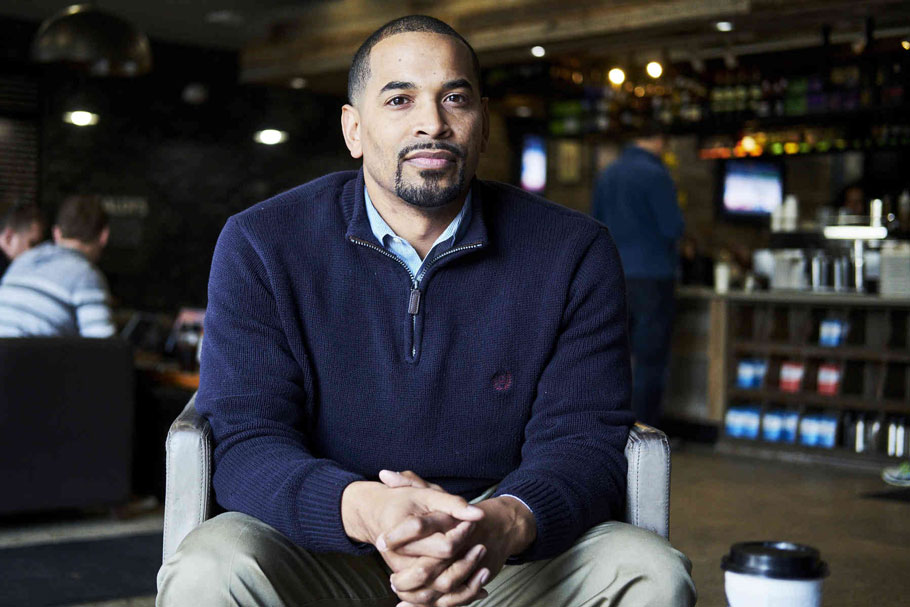

Will Jawando was raised in a low-income household in Silver Spring, Md. A lawyer and a former Obama White House staffer, he is among the rare black boys who reached the top fifth of the income distribution as an adult. T.J. Kirkpatrick for The New York Times
He was one of the 20 million children born between 1978 and 1983 whose lives are reflected in the study. Using census data that included tax files, the researchers were able to link the adult fortunes of those children to their parents’ incomes. Names and addresses were hidden from the researchers.
Previous research suggests some reasons there may be a large income gap between black and white men, but not between women.
Other studies show that boys, across races, are more sensitive than girls to disadvantages like growing up in poverty or facing discrimination. While black women also face negative effects of racism, black men often experience racial discrimination differently. As early as preschool, they are more likely to be disciplined in school. They are pulled over or detained and searched by police officers more often.
“It’s not just being black but being male that has been hyper-stereotyped in this negative way, in which we’ve made black men scary, intimidating, with a propensity toward violence,” said Noelle Hurd, a psychology professor at the University of Virginia.
She said this racist stereotype particularly hurts black men economically, now that service-sector jobs, requiring interaction with customers, have replaced the manufacturing jobs that previously employed men with less education.
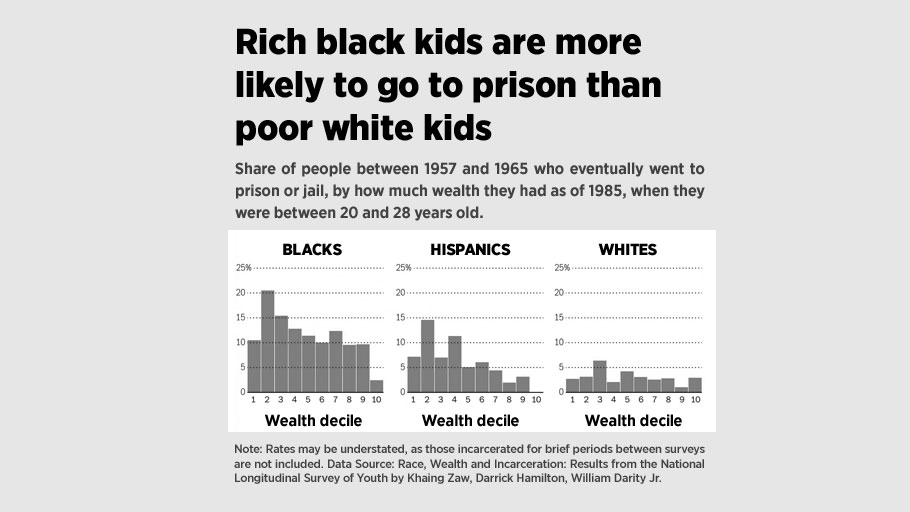
The new data shows that 21 percent of black men raised at the very bottom were incarcerated, according to a snapshot of a single day during the 2010 census. Black men raised in the top 1 percent — by millionaires — were as likely to be incarcerated as white men raised in households earning about $36,000.
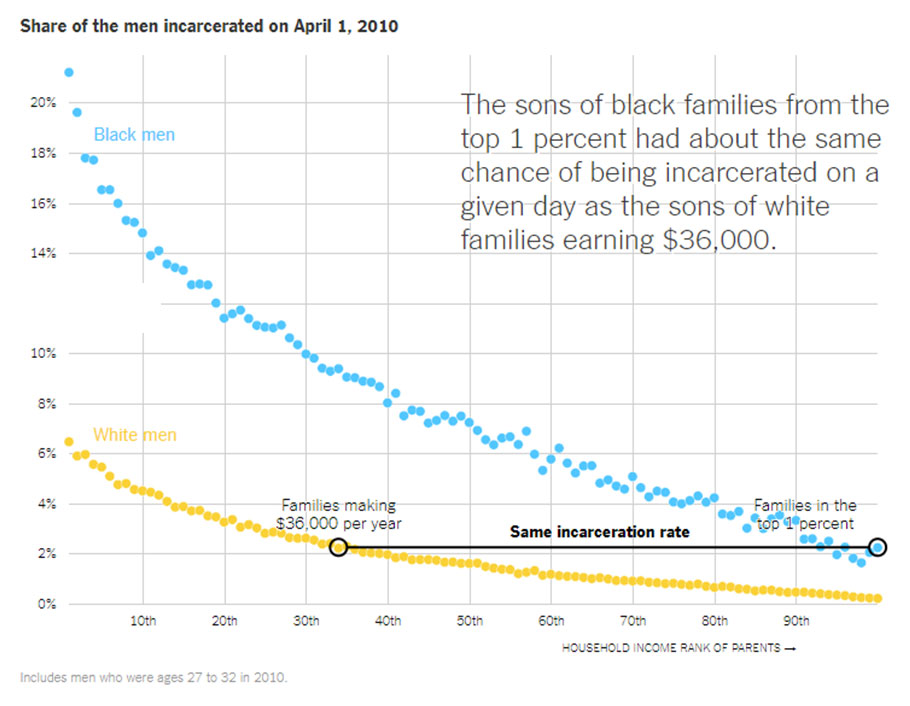 At the same time, boys benefit more than girls from adult attention and resources, as do low-income and nonwhite children, a variety of studies have found. Mentors who aren’t children’s parents, but who share those children’s gender and race, serve a particularly important role for black children, Ms. Hurd has found. That helps explain why the presence of black fathers in a neighborhood, even if not in a child’s home, appears to make a difference.
At the same time, boys benefit more than girls from adult attention and resources, as do low-income and nonwhite children, a variety of studies have found. Mentors who aren’t children’s parents, but who share those children’s gender and race, serve a particularly important role for black children, Ms. Hurd has found. That helps explain why the presence of black fathers in a neighborhood, even if not in a child’s home, appears to make a difference.
Some of the widest black-white income gaps in this study appear in wealthy communities. This fits with previous research that has shown that the effects of racial discrimination cross class lines. Although all children benefit from growing up in places with higher incomes and more resources, black children do not benefit nearly as much as white children do. Moving black boys to opportunity is no guarantee they can tap into it.
“Simply because you’re in an area that is more affluent, it’s still hard for black boys to present themselves as independent from the stereotype of black criminality,” said Khiara Bridges, a professor of law and anthropology at Boston University who has written a coming paper on discrimination against affluent black people.
This dynamic still weighs on Mr. Jawando. He has a good income, multiple degrees and political aspirations — he is running for county council in Montgomery County, where he grew up. But in his own community, he is careful to dress like a professional.
“I think if I’m putting on a sweatsuit, if I go somewhere, will I be seen as just kind of a hood black guy?” he said. “Or will people recognize me at all?” Those small daily decisions — to wear a blazer or not — follow him despite his success. “I don’t think you escape those things,” he said.
Other Findings From the Research
This study makes it possible to look in greater detail at interrelated disparities that researchers have long studied around income, marriage rates and incarceration. Here are some of the other findings.
There’s a large gap in the marriage rates of white and black Americans, even after accounting for income.
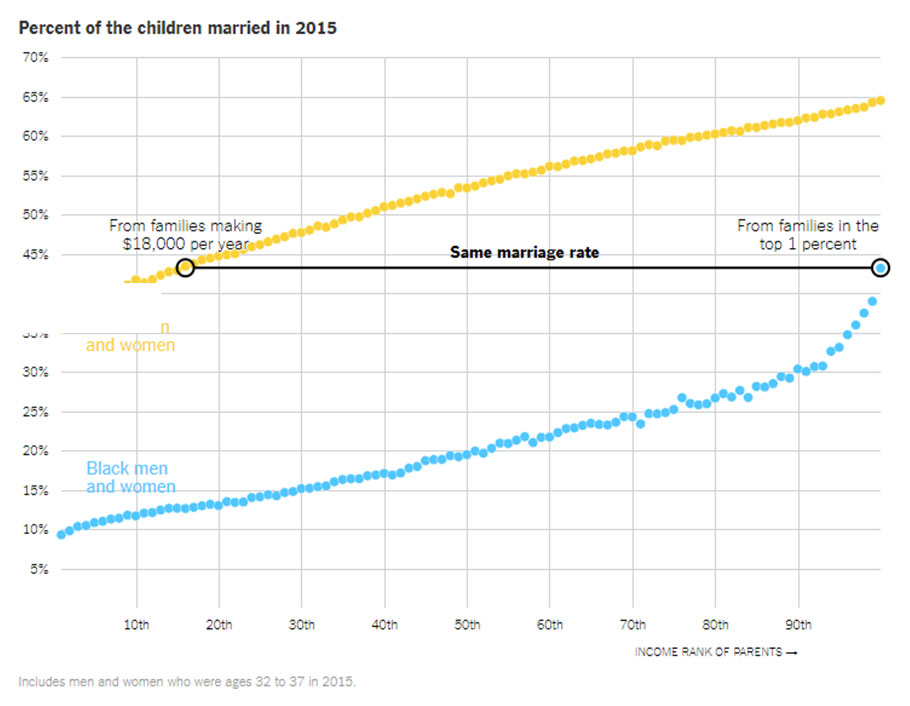 One reason income gaps between whites and blacks appear so large at the household level is that black men and women are less likely to be married. That means their households are more likely to have a single income — not two. For this reason and others, many point to differences in family structure as a primary driver of racial income inequality. If black children don’t have married parents, the argument goes, they’re more likely to grow up with fewer resources and less adult attention at home.
One reason income gaps between whites and blacks appear so large at the household level is that black men and women are less likely to be married. That means their households are more likely to have a single income — not two. For this reason and others, many point to differences in family structure as a primary driver of racial income inequality. If black children don’t have married parents, the argument goes, they’re more likely to grow up with fewer resources and less adult attention at home.
This study found, however, that broad income disparities still exist between black and white men even when they’re raised in homes with the same incomes and the same family structure.
The income gap exists for black and white boys if they had one parent in the house or two.
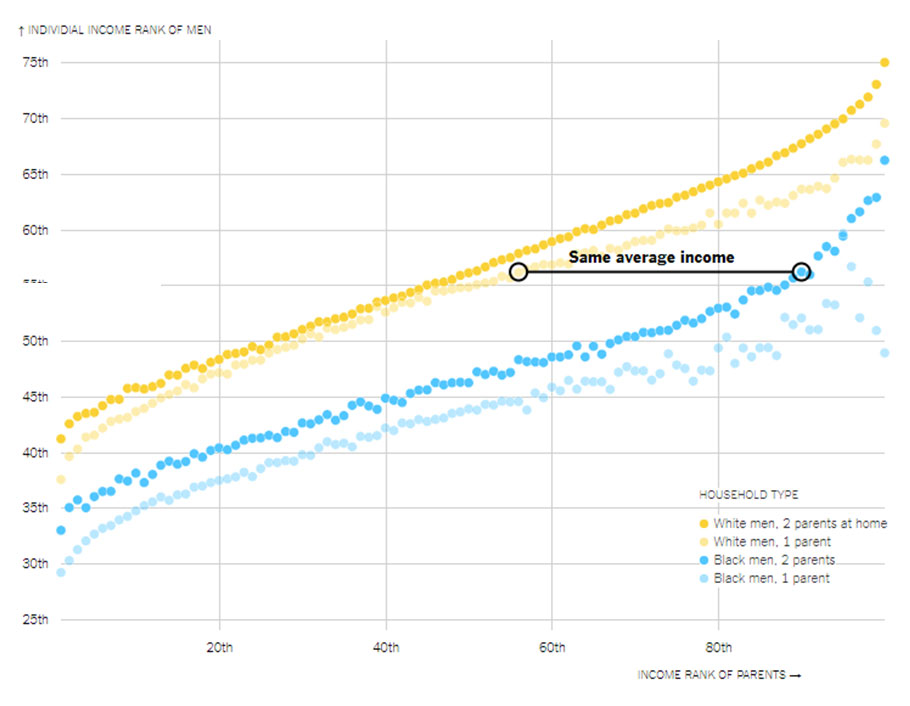 As this chart shows, a black man raised by two parents together in the 90th percentile — making around $140,000 a year — earns about the same in adulthood as a white man raised by a single mother making $60,000 alone.
As this chart shows, a black man raised by two parents together in the 90th percentile — making around $140,000 a year — earns about the same in adulthood as a white man raised by a single mother making $60,000 alone.
The high mobility rate for Asian-Americans is partly about immigration.
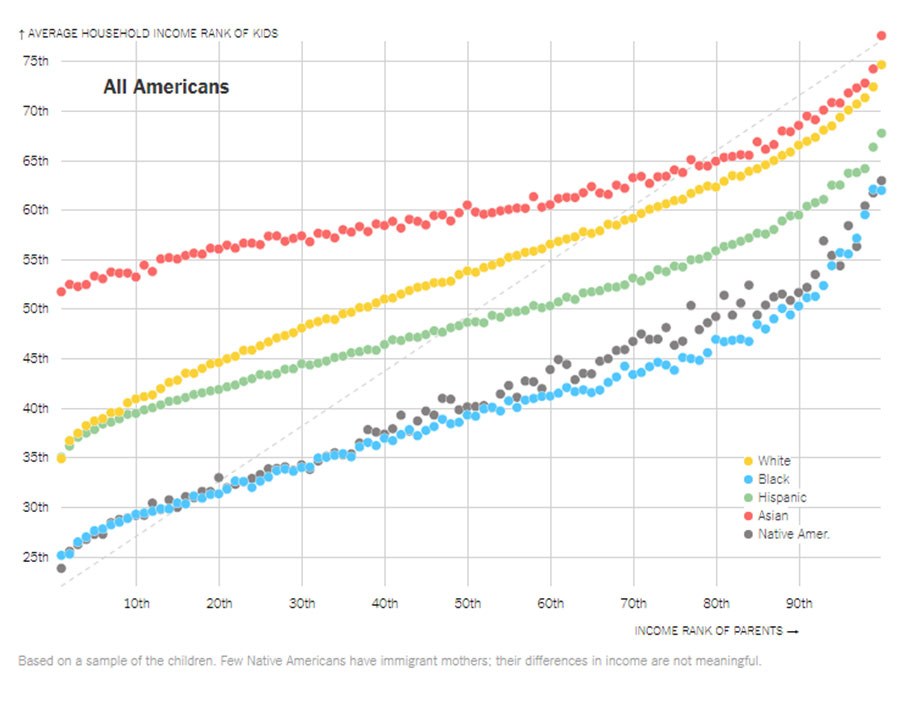
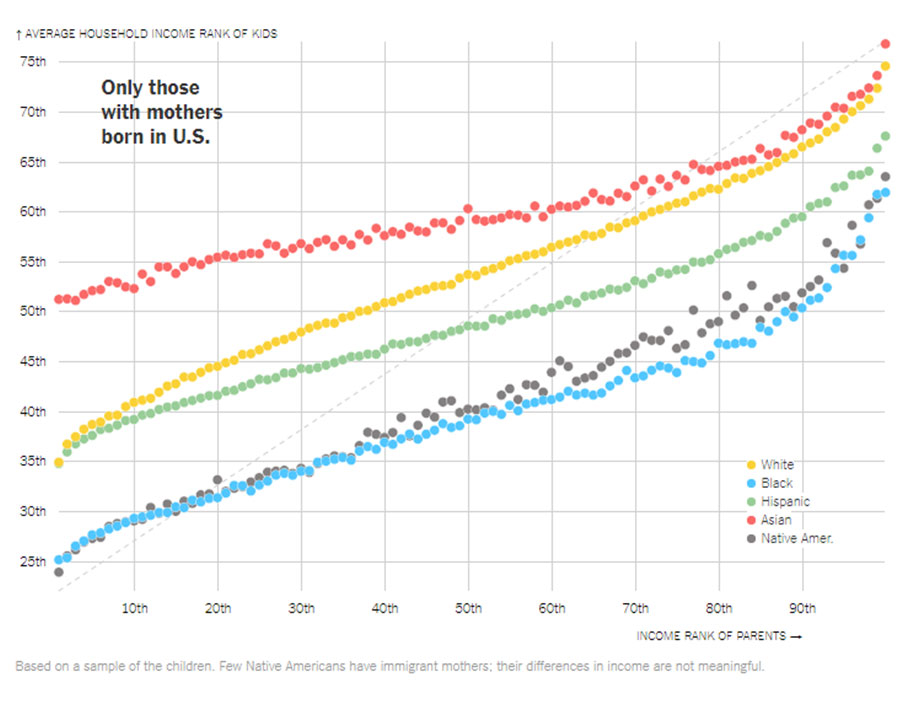 Asian-Americans earn more in adulthood than whites who were raised in families with similar incomes. But that advantage largely disappears when the researchers look only at children whose parents were born in the United States. Non-immigrant Asian-Americans fare about as well in the economy as whites. (The study did not divide Asian-Americans or Hispanics into smaller groups by country of origin, collapsing potentially significant differences between, say, Mexican-Americans and Puerto Ricans.)
Asian-Americans earn more in adulthood than whites who were raised in families with similar incomes. But that advantage largely disappears when the researchers look only at children whose parents were born in the United States. Non-immigrant Asian-Americans fare about as well in the economy as whites. (The study did not divide Asian-Americans or Hispanics into smaller groups by country of origin, collapsing potentially significant differences between, say, Mexican-Americans and Puerto Ricans.)
The worst places for poor white children are almost all better than the best places for poor black children.
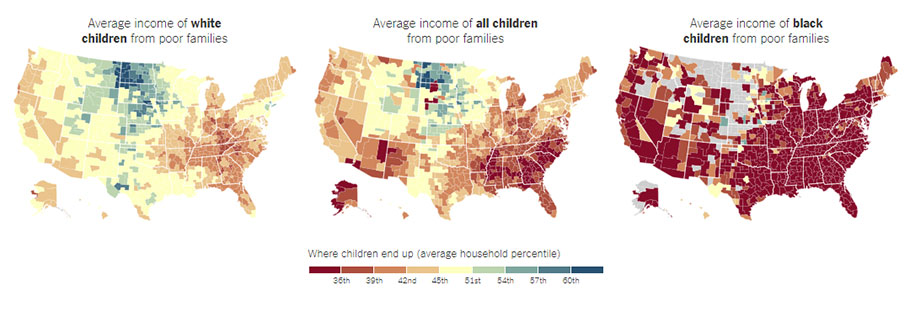 In previous work, some of these same researchers looked at how the prospects for poor children vary depending on where they grow up. The middle map above shows those earlier results: Poor children appeared to have less opportunity in the Southeast and more in the Northern Great Plains. With the new data, it’s now possible to look at the effects of geography separately for blacks and whites.
In previous work, some of these same researchers looked at how the prospects for poor children vary depending on where they grow up. The middle map above shows those earlier results: Poor children appeared to have less opportunity in the Southeast and more in the Northern Great Plains. With the new data, it’s now possible to look at the effects of geography separately for blacks and whites.
Poor white children struggle in parts of the Southeast and Appalachia. But they still fare better there than poor black children do in most of America. In effect, the worst places for whites produce outcomes that are about as good as the best places for blacks. These new maps also suggest that part of the reason the Southeast looks bad for all children, in the middle map, is that the region is home to many black children who fare particularly poorly there.
Very few nonwhite Americans started at the very top.
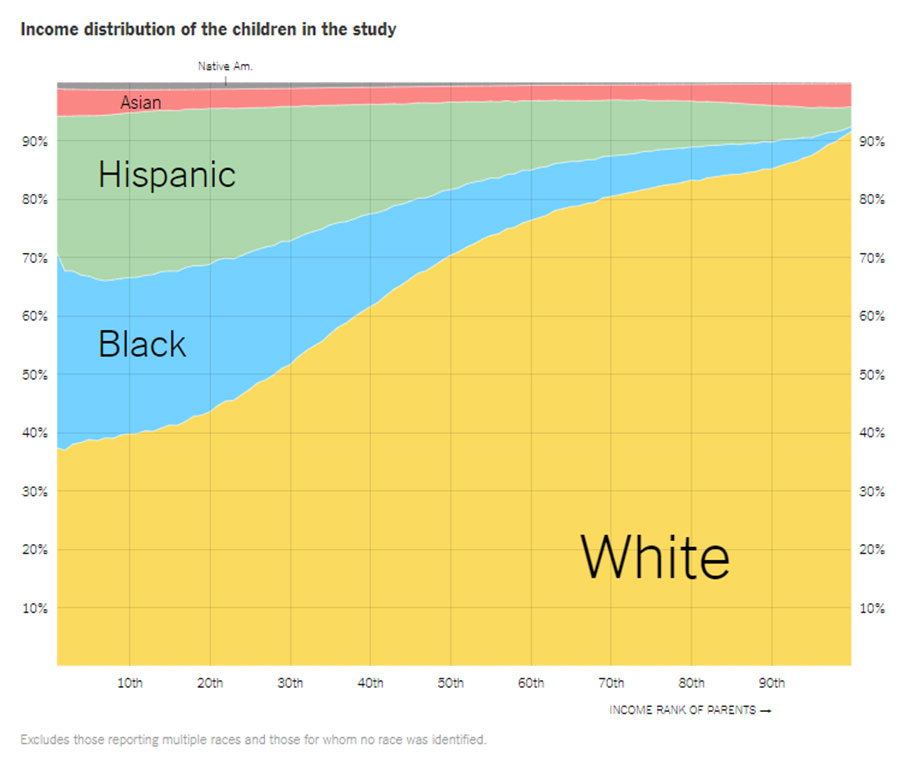 African-Americans made up about 35 percent of all children raised in the bottom 1 percent of the income distribution. They made up less than 1 percent of the children at the very top. This picture captures both a source of racial inequality and a consequence of it. White children are more likely to start life with economic advantages. But we now know that even when they start with the same advantages as black children, white boys still fare better, only reinforcing the disparities seen here.
African-Americans made up about 35 percent of all children raised in the bottom 1 percent of the income distribution. They made up less than 1 percent of the children at the very top. This picture captures both a source of racial inequality and a consequence of it. White children are more likely to start life with economic advantages. But we now know that even when they start with the same advantages as black children, white boys still fare better, only reinforcing the disparities seen here.
The Real Starting Positions
The ladder charts so far have shown equal numbers of black and white boys raised by rich or poor families — what would happen, in other words, if we started with 10,000 boys, and half were black and half white.
In reality, whites and blacks are not represented equally across the income spectrum. More than two-thirds of black boys are raised by poor or lower-middle-class families, while more than half of white boys are raised by rich or upper-middle-class families. The chart below depicts boys from every income quintile – not just the top or bottom ones – proportioned according to their real starting places in life.