
By Olivia B. Waxman,Time — After the Independence Day military parade in the nation’s capital on Thursday, President Donald Trump will give a speech at the Lincoln Memorial, the most…

By Olivia B. Waxman,Time — After the Independence Day military parade in the nation’s capital on Thursday, President Donald Trump will give a speech at the Lincoln Memorial, the most…
This 2009 documentary was produced by the Washington, DC Office of Cable Television to commemorate DC Emancipation Day. The film is a stirring account of African-American history from the colonial…

By Valerie Russ — Most Americans overwhelmingly oppose reparations to African Americans descendants of enslaved persons. But a slight uptick in support especially among younger Americans in recent years may be a result of activism over police killings over past five years.

This moving and profound portrait serves as a fitting biographical tribute as well as a piercing, often painful recount of African American history from slavery and the Civil War to the Jim Crow era, the Civil Rights movement and beyond. By Syreeta McFadden, The Atlantic — One of my white teachers in high school insisted that Toni Morrison would be confusing to me as a reader. So I approached the…

By Dr. Maulana Karenga — Usually when we want to confront and discount America’s founding myth of creating a democracy of free and equal persons, its hypocritical and high-hype claims…
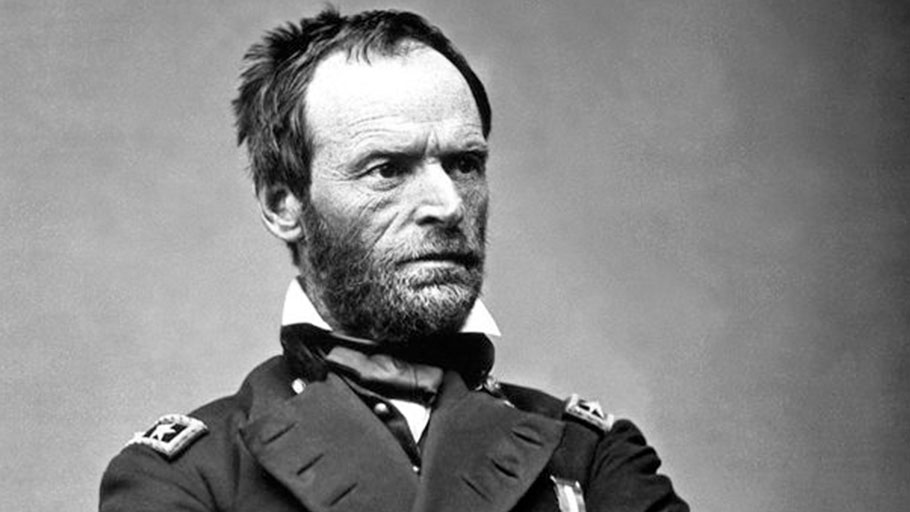

By Henry Louis Gates, Jr. — We’ve all heard the story of the “40 acres and a mule” promise to former slaves. It’s a staple of black history lessons, and it’s the name of Spike Lee’s film company. The promise was the first systematic attempt to provide a form of reparations to newly freed slaves, and it was astonishingly radical for its time, proto-socialist in its implications. In fact, such…
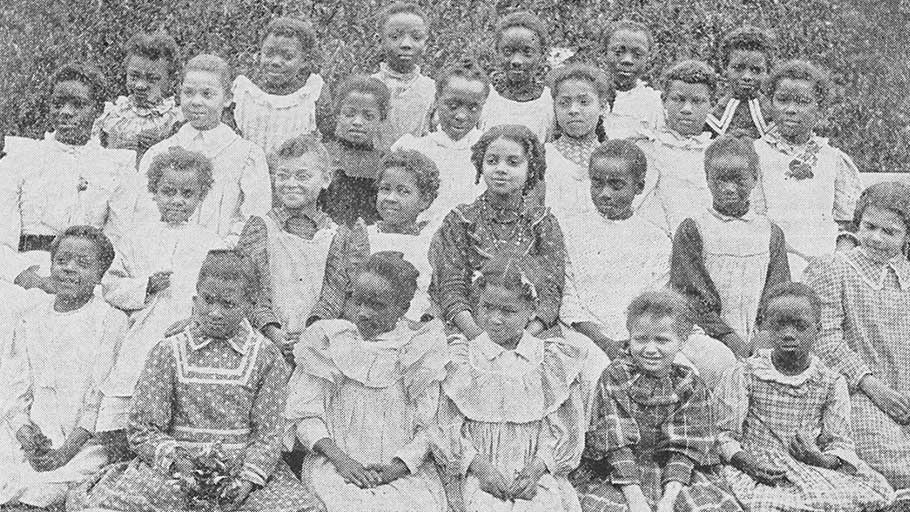

In one of the earliest examples of reparations, an ex-slave named Belinda petitioned the government and was granted an annuity. By Matthew Wills, JSTOR Daily — Inspired in part by journalist Ta-Nehisi Coates, conversations about reparations for slavery and its aftermath have become mainstream. But they aren’t new: Reconstruction’s unfulfilled promise of “forty acres and a mule” had antecedents dating back to America’s founding. Belinda was a slave under Royall…

By The Real News Network — This week, the first congressional hearing on reparations in nearly 12 years was held on Capitol Hill. As the discussion on reparations matures, what needs to happen politically for the effort to move forward? Story Transcript TA-NEHISI COATES For a century after the Civil War, black people were subjected to a relentless campaign of terror. A campaign that extended well into the lifetime of…
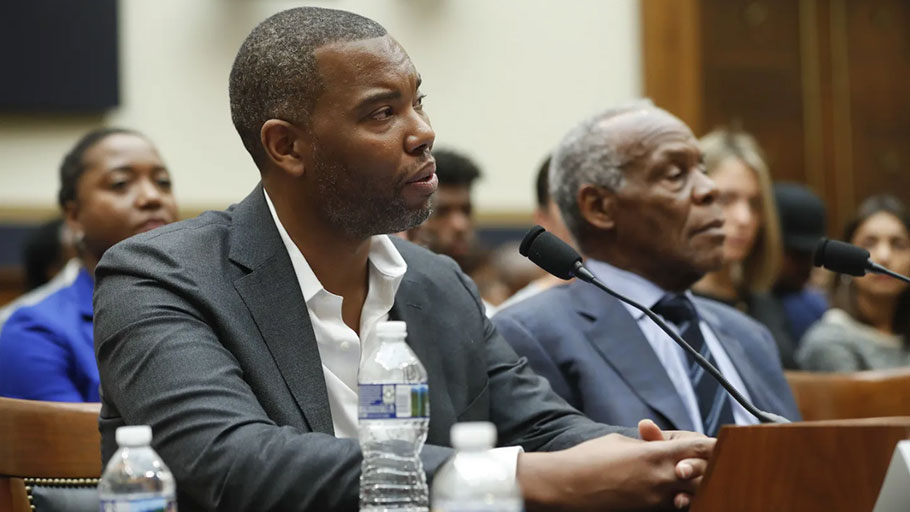

HR 40 calls the country to account for racist predation inflicted upon black folks living and dead. By Aaron Ross Coleman, The Nation — When I saw a little black boy standing outside the Rayburn House Office Building holding a placard that read “Cut the Check—MLK,” I knew it was going to be an extraordinary day in Washington, DC. This Juneteenth, Congress held its first hearing on the resolution to…
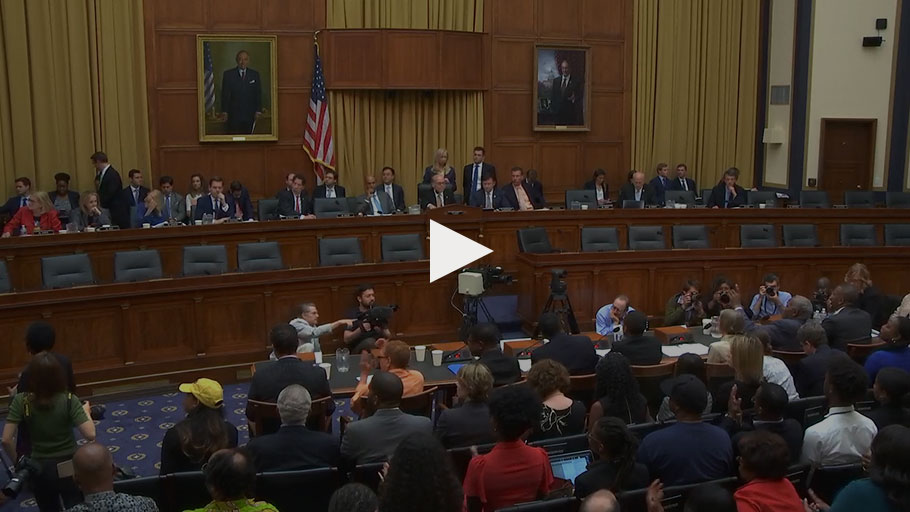
Full Video: Washington, DC — On June 19, 2019 (Juneteenth), the House Judiciary Subcommittee on the Constitution, Civil Rights, and Civil Liberties held a hearing on H.R. 40, the Commission to Study and Develop Reparation Proposals for African-Americans Act. The purpose of the hearing was to examine, through open and constructive discourse, the legacy of the trans-Atlantic slave trade, its continuing impact on the community and the path to restorative justice.…

Originally published 6.19.19 by The Takeaway, WNYC Studios — On this Juneteenth, or June 19, we celebrate the end of slavery in the United States 154 years ago. Members of Congress chose this symbolic day to hold hearings on a reparations bill. The bill, if it passes, will establish a commission to determine whether — and if so, how — the US government owes anything to the descendants of enslaved people. To…
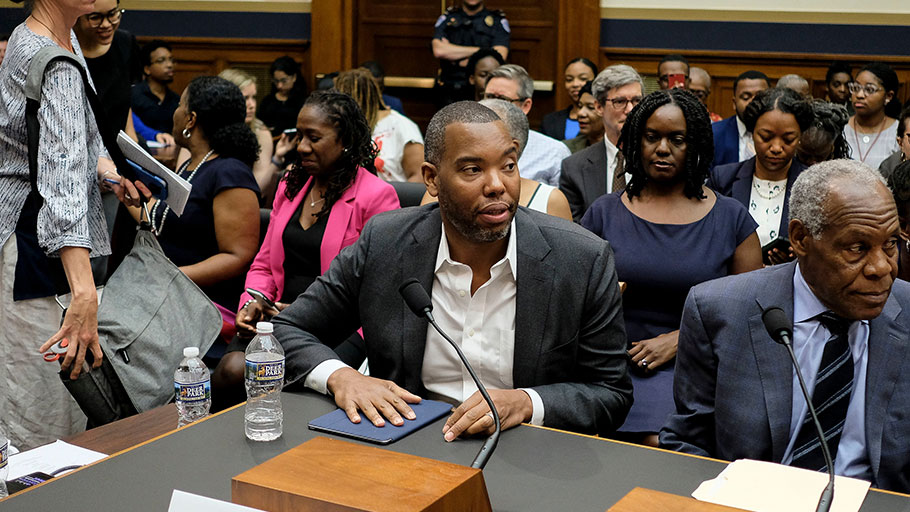

By The New York Times — The writer argued that African-Americans were exploited by nearly every American institution, before and after slavery ended. Ta-Nehisi Coates, whose 2014 article “The Case for Reparations” in The Atlantic rekindled the…